If you have diabetes, you are either not producing enough insulin, or your insulin is not functioning the way it should. When you eat, your blood glucose levels rise. Your pancreas releases insulin that allows your body to store this sugar to use later. In a person with diabetes this process doesn’t work properly. It can result in your blood sugar levels rising either too high, resulting to hyperglycaemia or dropping too low, resulting to hypoglycaemia.
People with Type 1 diabetes normally rely on insulin treatments to control their blood glucose levels, and they can take insulin through either a pump or an injection. People with Type 1 diabetes are usually diagnosed earlier in life and it is not known to be linked to age, weight or lifestyle factors.
Type 2 diabetes is a condition where the insulin your body makes does not work properly, or it cannot make enough insulin. It is usually diagnosed later in life. Many people with Type 2 diabetes are able to carry on without insulin injections, but may need to make a few lifestyle changes such as:
- Increasing exercise
- Losing weight
- Changing their eating habits
However, if lifestyle changes do not have a great enough impact then people with Type 2 diabetes may progress from oral medication to injectables and/or insulin through injections or pumps.
There are 3 common types of insulin someone could be prescribed which are listed below:
- Rapid-acting/short-acting is usually taken before your regular meals to protect your glucose levels from rising while eating.
- Intermediate-acting is also known as background insulin or basal insulin. This means it works throughout the day. It is often combined with rapid-acting or short-acting insulin.
- Long-acting is slower than intermediate insulin, but very similar in how your body processes it. It is often combined with rapid-acting or short-acting insulin.
The type of insulin you are prescribed will depend on your body’s needs.

You will be advised the best times to take your insulin by your healthcare professional. It’s important to adhere to these instructions to control your blood glucose levels.
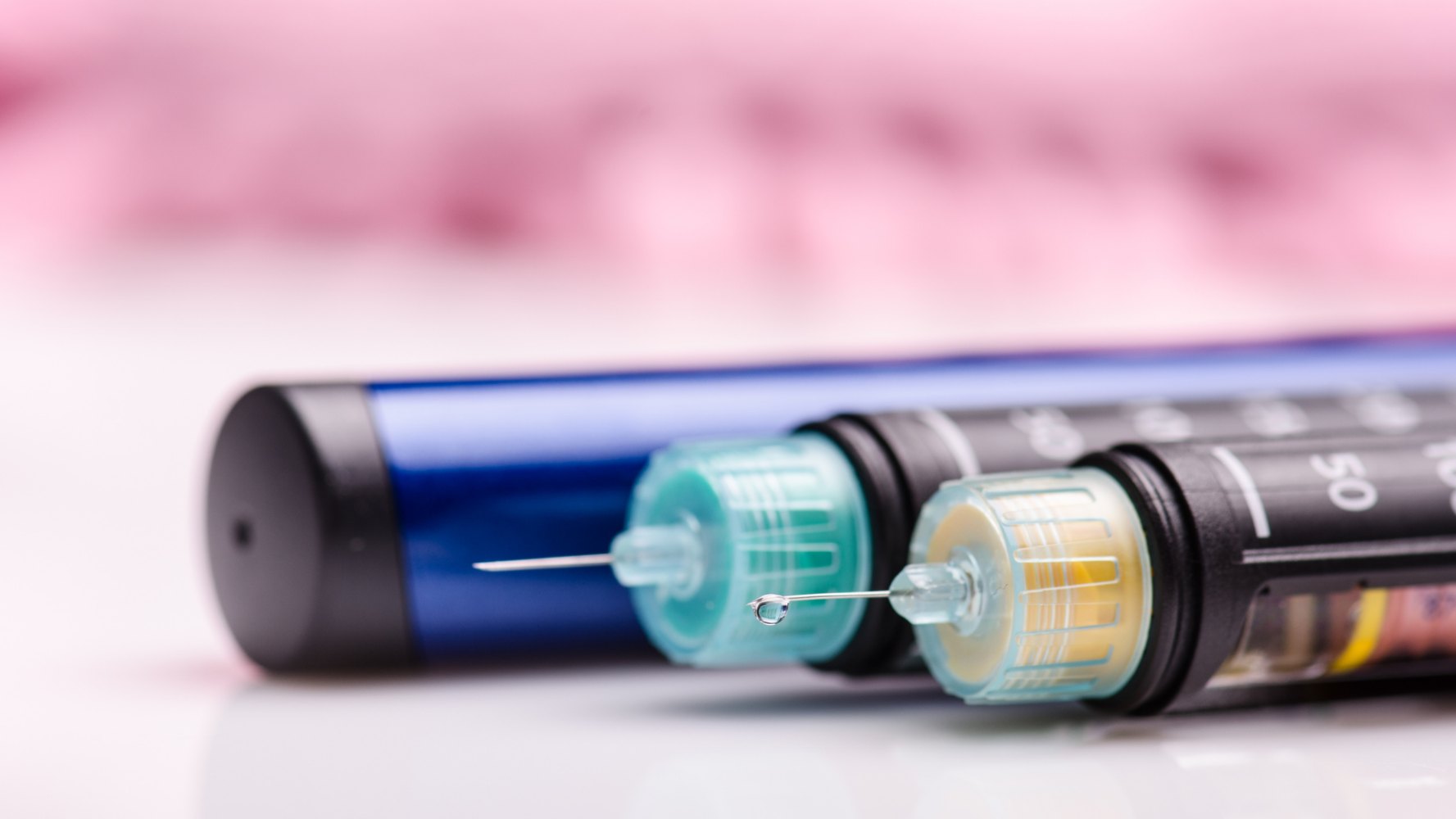
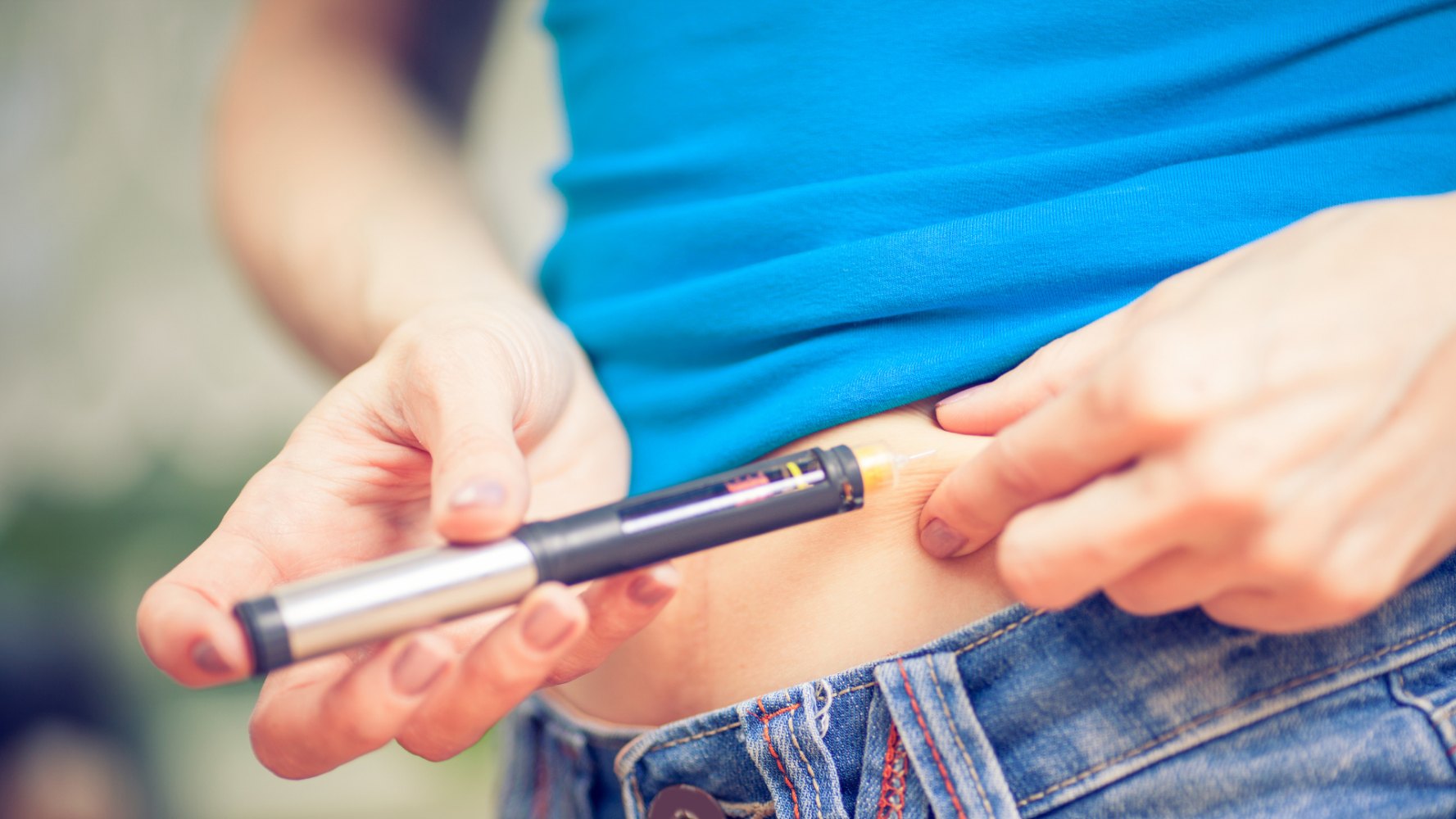
Insulin doesn’t come in pill form because your digestive system would break it down before it had a chance to start working. Many people with diabetes who use insulin will self-administer it by injecting it with a pre-filled insulin pen. If you inject regularly you will need to vary the areas of your skin where you inject to ensure your insulin is being absorbed consistently.
The ideal areas to inject insulin are the parts of your body with a larger layer of fat, such as:
- Abdomen
- Thighs
- Buttocks
If you inject in the same place too often, your skin may start to become stiffer, this can often lead to it becoming lumpy. It can help to imagine a grid drawn onto your body so you can pick a different square to inject into each time. After some time, you’d need to start again at the first square you chose, but that should have fully healed by the time you’ve gone back to that area.
Some areas of your body will absorb insulin quicker than others so it’s important to keep track of this. Speak to your healthcare professional if you have any concerns about your insulin injection sites and they will be able to advise you.
How should I store my insulin?
It’s important to store your insulin properly to make sure it is effective:
- Insulin should be stored in the fridge and away from heat. If you go out your insulin will be useable at room temperature for short periods of time, but if you’re travelling it’s best to keep it in a cool bag.
- Keep your insulin out of sunlight.
- Check the expiry date on your insulin and don’t use it if it’s out of date.
How can Spirit Pharmacy help you?
Leicester
Leicestershire
LE2 6UP
